Introduction to Boost Glide (B/G) Events – Cast Glider L-Hooks for B Boost Glide
Introduction to Boost Glide (B/G) Events
Boost Glide (B/G) events represent one of the most technically demanding and rewarding disciplines in model rocketry, combining the precision of powered flight with the artistry of unpowered gliding to achieve maximum flight duration. These events challenge competitors to optimize every aspect of their designs, from the initial rocket boost to the final glide phase, creating a comprehensive test of engineering skill and aeronautical understanding.
In B/G competition, participants use B-class motors to propel a glider to altitude, where it transitions from powered flight to sustained unpowered glide. The objective is to maximize the total flight time from launch to landing, requiring careful optimization of both the boost and glide phases to achieve the best possible performance. This dual-phase flight profile distinguishes B/G from other rocketry events and creates unique design and operational challenges.
The appeal of B/G events lies in their perfect blend of technical complexity and accessible entry requirements. While achieving competitive performance demands sophisticated engineering and meticulous attention to detail, the basic principles can be understood and applied by enthusiasts at all levels. This accessibility has helped B/G maintain a strong following in the model rocketry community for decades.
The Role of the L-Hook in the Boost-to-Glide Transition
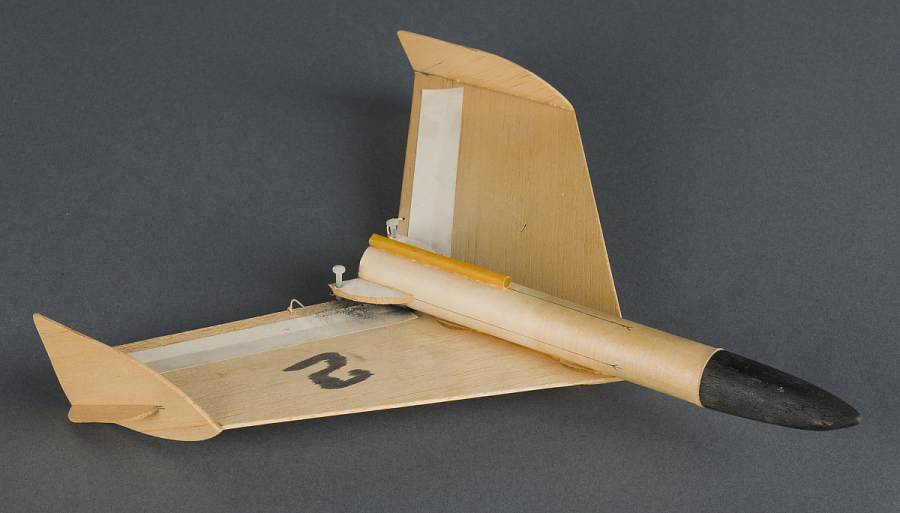
The L-hook represents one of the most critical components in successful B/G flights, serving as the mechanical interface between the rocket booster and the glider during the crucial transition from powered to unpowered flight. This small but essential component must reliably hold the glider during boost while releasing cleanly at the appropriate moment to allow successful transition to glide.
Functional Requirements
The L-hook must withstand significant forces during the boost phase, including acceleration loads from the motor thrust and aerodynamic forces from flight through the atmosphere. These forces can be substantial, particularly with high-thrust B-class motors, requiring careful design and construction to prevent failure.
Release reliability is equally critical, as any failure to separate at the proper moment can result in poor glide performance or complete mission failure. The L-hook must release cleanly without imparting excessive disturbance to the glider’s flight path, ensuring smooth transition to stable glide.
Weight optimization is essential for L-hook design, as any unnecessary mass reduces the payload capacity available for the glider. This optimization becomes particularly important in competitive events where maximum glider performance is critical for success.
Design Considerations
Material selection for L-hooks involves balancing strength, weight, and cost considerations. Traditional materials such as steel or aluminum provide excellent strength but may add unwanted weight, while lighter materials such as plastics or composites offer weight savings but may compromise durability.
Geometry optimization affects both structural performance and release characteristics. The hook shape must provide adequate retention strength while allowing for clean separation when the retention pin or other release mechanism is activated.
Manufacturing precision is critical for consistent performance, as variations in dimensions or surface finish can affect both strength and release reliability. High-quality manufacturing processes and quality control procedures are essential for competitive L-hook components.
Consider the interaction between the L-hook and the glider’s release mechanism during the design process. The hook geometry should complement the glider’s release system to ensure smooth, reliable separation under all expected flight conditions.
Integration with Glider Design
L-hook placement on the glider affects both aerodynamic performance and structural integrity. The hook must be positioned to minimize aerodynamic interference while providing adequate structural support for the loads experienced during boost.
Load path analysis ensures that forces transmitted through the L-hook are properly distributed through the glider structure without creating stress concentrations or failure points. This analysis is particularly important for lightweight gliders where structural margins may be minimal.
Recovery system integration must account for the L-hook’s presence and ensure that parachute or streamer deployment is not compromised by the hook or its attachment points. This integration may require special consideration in glider design and component placement.
Why Custom Casting is Advantageous
Custom casting of L-hooks offers significant advantages over commercially available alternatives, allowing competitors to optimize every aspect of hook design for their specific glider configurations and flight requirements. This customization capability can provide measurable performance improvements that translate directly into competitive advantage.
Performance Optimization Benefits
Weight reduction through custom casting allows for optimization of hook geometry and material distribution to achieve minimum weight while maintaining required strength. This optimization can free up payload capacity for additional glider performance features or improved recovery systems.
Geometry customization enables optimization of hook shape for specific glider designs and release mechanisms. Custom hooks can be designed to provide optimal retention strength while minimizing aerodynamic drag or structural interference.
Material selection flexibility allows competitors to choose from a wide range of casting materials to optimize for specific performance requirements. This flexibility extends beyond standard commercial offerings to include specialized alloys or composite materials that may provide unique advantages.
Economic Advantages
Cost effectiveness becomes apparent when considering the performance benefits and longevity of custom-cast components. While initial investment in casting equipment and materials may be higher than purchasing commercial hooks, the ability to produce multiple optimized components can provide significant cost savings over time.
Rapid prototyping capabilities allow for quick iteration and testing of new designs without the time and expense of ordering custom-machined components. This capability is particularly valuable during the development phase when design changes are frequent.
Replacement part production eliminates dependence on commercial suppliers for critical components. This independence can be crucial for maintaining competition readiness when commercial sources are unavailable or backordered.
Custom casting requires significant initial investment in equipment, materials, and learning time. Evaluate whether the performance benefits and long-term cost savings justify this investment for your specific competitive goals and usage patterns.
Quality Control and Consistency
Process control in custom casting allows for consistent production of high-quality components with known characteristics. This control can provide greater confidence in component performance than relying on commercially sourced parts of unknown quality or manufacturing history.
Inspection and testing capabilities enable verification of component properties and performance before use in competition. This verification can identify potential issues before they affect flight performance or safety.
Design modification flexibility allows for rapid implementation of improvements or adaptations based on flight experience or changing competition requirements. This flexibility can provide significant competitive advantages over competitors dependent on fixed commercial designs.
B/G Event Fundamentals
Understanding the fundamental principles of B/G events is essential for successful participation and competitive performance. These principles encompass not only the technical aspects of rocket and glider design but also the strategic considerations that distinguish winning entries from merely functional ones.
Flight Profile Characteristics
The B/G flight profile consists of three distinct phases: boost, transition, and glide. Each phase presents unique challenges and optimization opportunities that must be carefully balanced to achieve maximum total flight time.
During the boost phase, the rocket motor provides thrust to accelerate the combined vehicle to separation velocity. This phase typically lasts only a few seconds but determines the initial conditions for the subsequent glide phase.
The transition phase occurs immediately after separation when the glider establishes stable flight attitude and configuration. This phase is critical for successful mission completion, as any failure to achieve stable flight results in immediate mission termination.
The glide phase comprises the majority of total flight time and represents the primary opportunity for performance optimization. Glide performance depends on factors such as lift-to-drag ratio, wing loading, and atmospheric conditions.
Competition Rules and Constraints
| Rule Category | Key Requirements |
|---|---|
| Motor Class | Restricted to B-class motors (1.25-2.5 Newton-seconds total impulse) |
| Vehicle Configuration | Must separate into distinct booster and glider components |
| Flight Objective | Maximize total flight time from launch to landing |
| Recovery | Must include recovery system for safe landing |
| Safety | Must comply with all applicable safety regulations |
Performance Optimization Strategies
Boost phase optimization focuses on achieving maximum separation velocity and altitude while maintaining stable flight. This optimization involves motor selection, vehicle mass distribution, and aerodynamic design considerations.
Transition optimization ensures reliable separation and stable flight initiation. This optimization requires careful attention to center of gravity and center of pressure relationships, as well as separation mechanism design and timing.
Glide phase optimization maximizes lift-to-drag ratio and minimizes sink rate through careful attention to wing design, airfoil selection, and flight trim. This optimization represents the primary opportunity for performance differentiation in competition.
Equipment and Tool Requirements
Successful participation in B/G events requires careful selection and maintenance of specialized equipment and tools. This equipment encompasses everything from basic construction tools to sophisticated measurement and testing devices necessary for competitive performance.
Basic Construction Equipment
Fundamental construction tools include precision measuring instruments, cutting tools, and adhesive application equipment necessary for accurate component fabrication. These tools must be maintained in good condition to ensure consistent results.
Specialized tools for L-hook casting include mold-making materials, casting equipment, and finishing tools necessary for producing high-quality custom components. These tools represent a significant investment but provide unique capabilities for performance optimization.
Testing equipment such as scales, calipers, and timing devices enable verification of component properties and flight performance. This equipment is essential for optimizing designs and maintaining competitive readiness.
Safety Equipment and Procedures
Personal protective equipment including safety glasses, gloves, and ventilation equipment is essential for safe casting operations. These items protect against chemical exposure, thermal hazards, and physical injury during equipment use.
Fire safety equipment including extinguishers and fire blankets should be readily available when working with flammable materials or high-temperature processes. Proper fire safety procedures should be established and regularly practiced.
First aid supplies and emergency procedures should be established for all casting activities. Personnel should be trained in basic first aid and know how to respond to common workshop injuries or chemical exposures.
Always read and follow manufacturer safety instructions for all materials and equipment. Maintain current safety data sheets for all chemicals and materials used in casting operations.
Getting Started in B/G Competition
Beginning participation in B/G competition requires careful planning and preparation to ensure both safety and competitive success. New competitors should approach this challenging discipline with realistic expectations and a commitment to learning proper techniques and procedures.
Learning Resources and Mentorship
Experienced competitors and mentors can provide invaluable guidance for newcomers to B/G events. These resources offer practical insights into design techniques, construction methods, and competition strategies that are difficult to learn from written materials alone.
Published resources including books, magazines, and online forums provide comprehensive information about B/G principles and techniques. These resources can supplement hands-on learning and provide reference materials for ongoing development.
Workshops and training events offer opportunities to learn from experts and practice techniques in a structured environment. These events can accelerate learning and provide networking opportunities with other competitors.
Initial Investment Planning
Equipment investment planning should balance immediate needs with long-term goals to avoid unnecessary expenditures while ensuring adequate capabilities for competitive performance. This planning should consider both basic requirements and advanced capabilities that may be needed for future development.
Starting with proven designs and components can reduce initial risk and accelerate learning while building experience with fundamental principles. This approach allows newcomers to focus on learning proper techniques rather than troubleshooting design issues.
Budget planning should account for ongoing costs including materials, equipment maintenance, and competition entry fees. These costs can add up quickly and should be considered when evaluating the overall commitment required for competitive participation.













Post Comment